HD results from genetically programmed degeneration of nerve cells, called neurons, in certain areas of the brain. This degeneration causes uncontrolled movements, loss of intellectual faculties, and emotional disturbance. Specifically affected are cells of the basal ganglia, structures deep within the brain that have many important functions, including coordinating movement. Within the basal ganglia, HD especially targets neurons of the striatum, particularly those in the caudate nuclei and the pallidum. Also affected is the brain's outer surface, or cortex, which controls thought, perception, and memory.
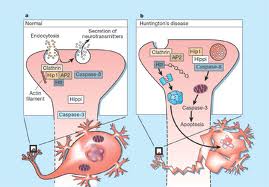
Involves disturbance in neurotransmitter substance primarily: Gamma Aminobyutric Acid (GABA) & Dopamine
GABA neurons in basal ganglia, frontal cortex and cerebellum are destroyed
GABA neurotransmitter production
Excess of dopamine causes abnormal neurotransmission along the affected pathway
Chorea and mental deterioration
Enlargement of the ventricles in HD patients due to atrophy of
the head of the caudate from neuronal loss.
the head of the caudate from neuronal loss.





Walang komento:
Mag-post ng isang Komento